Summary
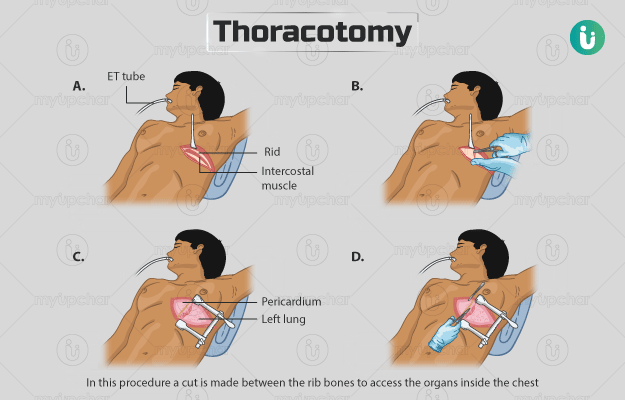
Thoracotomy procedure involves cutting an area between ribs to operate on the organs inside the chest. This surgery is performed if you have broken ribs or any issue with the lungs like lung cancer or infection. Before the procedure, the surgeon will assess your overall health and ask you about your habits and daily medicines. You will not be able to drink or eat anything from the night before the surgery. The surgeon will give you general anaesthesia to keep you asleep dueing the operation. You can go home five to seven days after the surgery. You will need to take care of the wound when you return home. If you experience any unusual symptoms like pain or breathing problem, inform your doctor immediately.