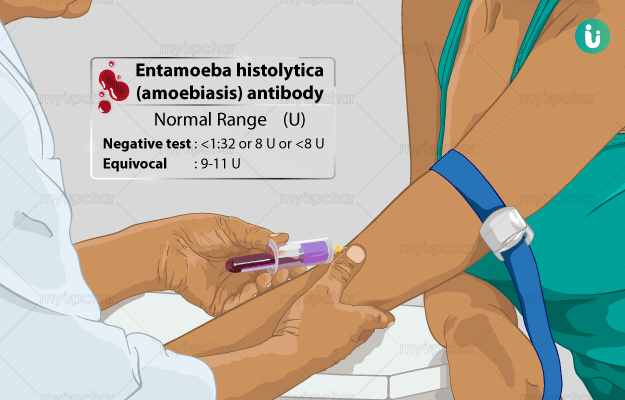
What is Entamoeba histolytica (Amoebiasis) Antibody test?
Entamoeba histolytica (E. histolytica) is a parasitic organism that causes amoebic dysentery or amoebiasis. The parasite enters the body in the form of cysts, which are present in unhygienic or contaminated food and water, and gets lodged inside the intestines. It then damages the intestinal cells, leading to the symptoms such as diarrhoea, pain in the abdomen, and fever. People who get amoebic dysentery, produce specific type of antibodies against E. histolytica to destroy this invading organism.
An E. histolytica antibody test detects and measures the number of anti-entamoeba histolytica antibodies in the blood. Although our body produces various types of antibodies against this pathogen, the test only evaluates IgG antibodies as they give the correct evaluation of the patient’s condition.