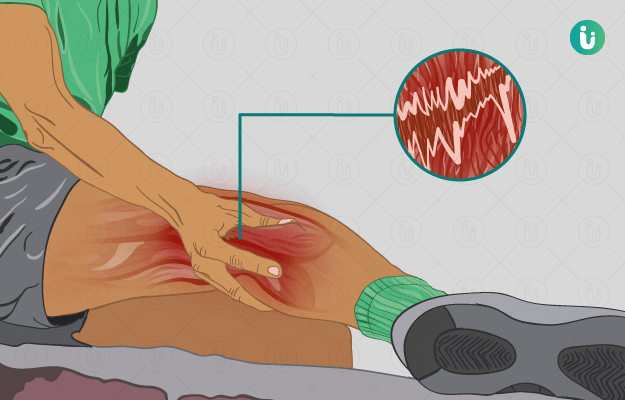
What is muscle strain?
A muscle strain is a type of injury to one or more muscles. A person is said to have a muscle strain when the muscle fibres undergo stretching or tearing. Most muscle strains are mild and the muscle fibres remain strong and intact. The muscle fibres stretch beyond its limits and tear only in a few cases of muscle strain.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The main signs and symptoms of a muscle strain are:
- A popping sensation in the muscle at the time of injury
- Muscle spasms or cramps
- Muscle tenderness and pain
- Swelling in the muscle
- Discolouration at the site of injury
- Inflammation
What are the main causes?
The main causes of a muscle strain are:
- Overstretching of hamstring muscles during activities like dancing or sprinting
- Excessive twisting or jumping causes a strain in the back muscles
- Sports injuries
- Lifting heavy weights
- Poor posture
- Not warming up before physical activities
How is it diagnosed and treated?
A muscle strain is diagnosed by the following methods:
- A doctor will ask you to note down symptoms experienced related to the movement and strength of the muscle.
- Spasms, weakness and muscle tenderness will be checked and compared with the medical history.
- An X-ray or MRI scan may be ordered, if needed.
- Additional tests may be recommended to look for problems in the spinal cord and vertebral discs.
Muscle strains are treated using the following methods:
- Rest, ice application, compression using a crepe bandage or cloth and elevation at or above heart level (RICE) is the most common method used to treat a muscle strain. These help to reduce swelling and pain.
- Mild strains are treated using physical therapy that strengthens the muscle as the strain heals.
- Severe muscle strains may need surgery, followed by physical therapy.
- A doctor may also recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), painkillers or muscle relaxants to provide relief from swelling and pain.
- Activity restrictions and use of cast, splint, wheelchair or crutches are other treatment options.

 Doctors for Muscle Strain
Doctors for Muscle Strain  OTC Medicines for Muscle Strain
OTC Medicines for Muscle Strain